If you’ve ever stocked your pond with healthy fingerlings and returned days later to find unexplained deaths, you’re not alone. Losing catfish fingerlings is one of the most frustrating and…

Organic agricultural products right to your table!

If you’ve ever stocked your pond with healthy fingerlings and returned days later to find unexplained deaths, you’re not alone. Losing catfish fingerlings is one of the most frustrating and…
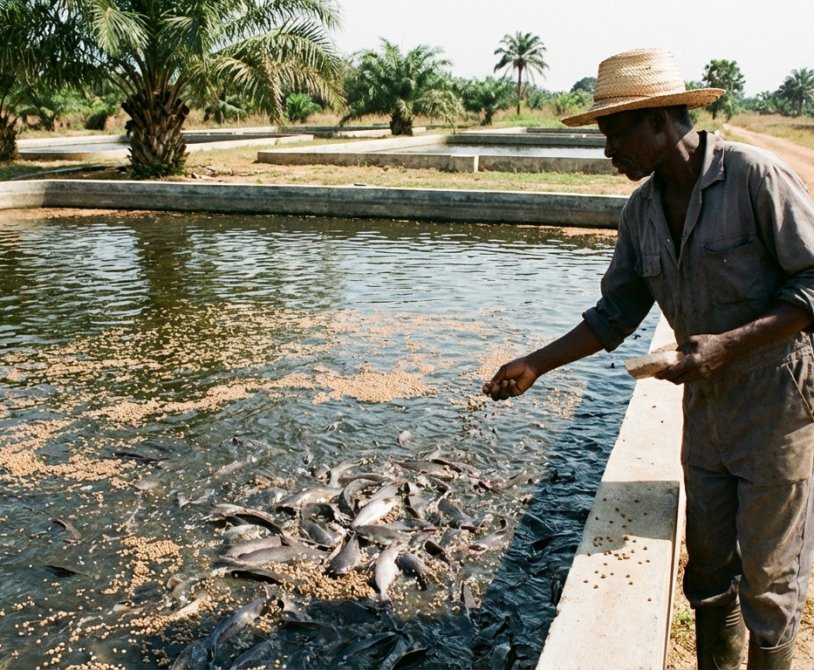

Feeding is the most important factor in successful catfish farming. In fact, feed alone can account for 60–70% of your production cost, which means proper feeding management can determine whether…
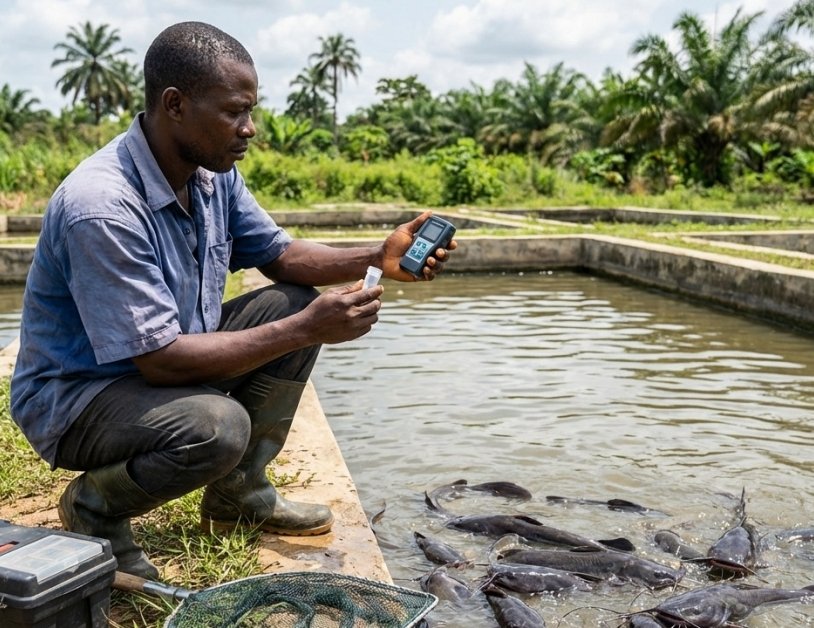

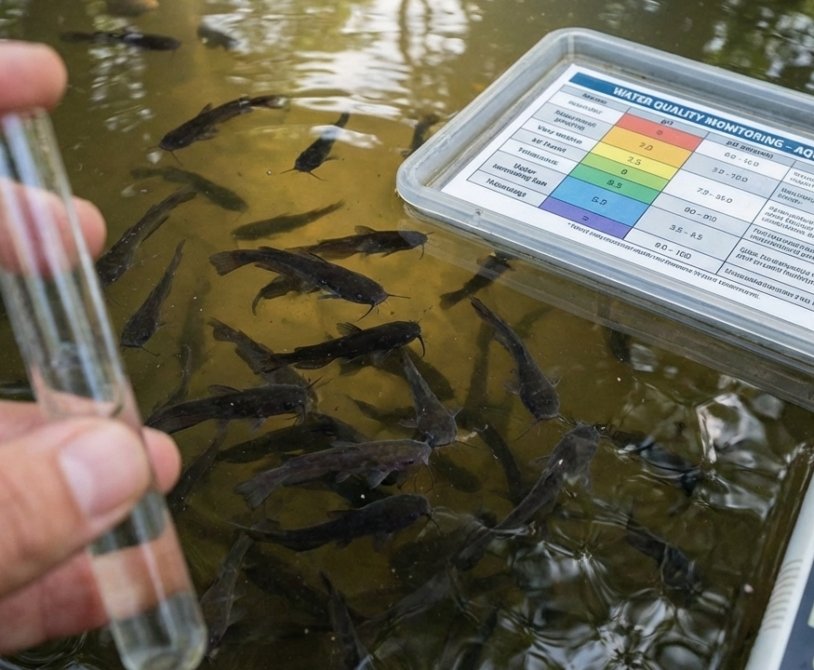
Keeping optimal water quality is the most critical factor for successful aquaculture. Whether you manage a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS), earthen ponds, or tanks for catfish and tilapia, the chemical…
Starting a fish farm is an exciting venture, but a pond is more than just a hole filled with water—it is a living ecosystem. Successful pond management is the art…
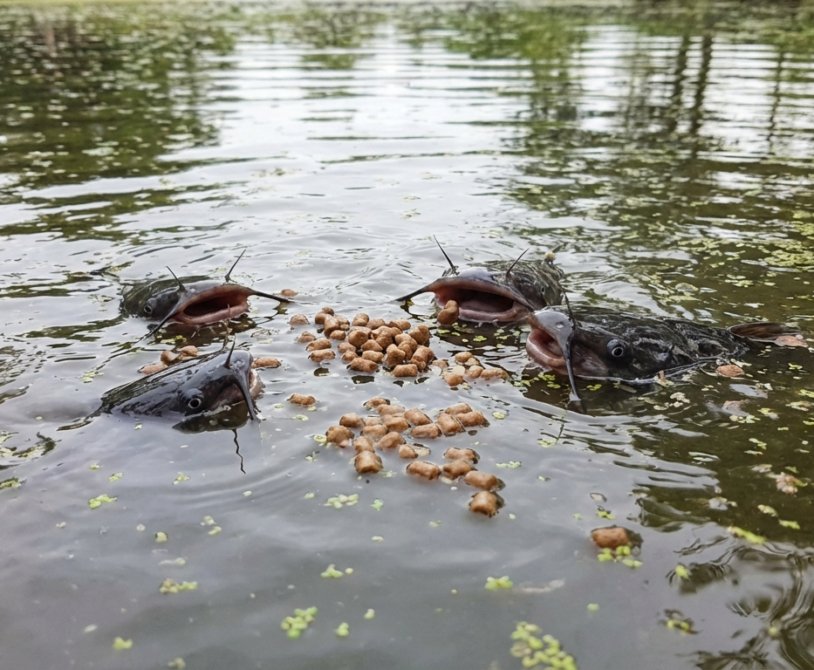

In commercial aquaculture, nutrition represents roughly 60-70% of total operational costs. Feeding is the single most important factor determining your Average Daily Gain (ADG) and overall farm profitability. Even with…
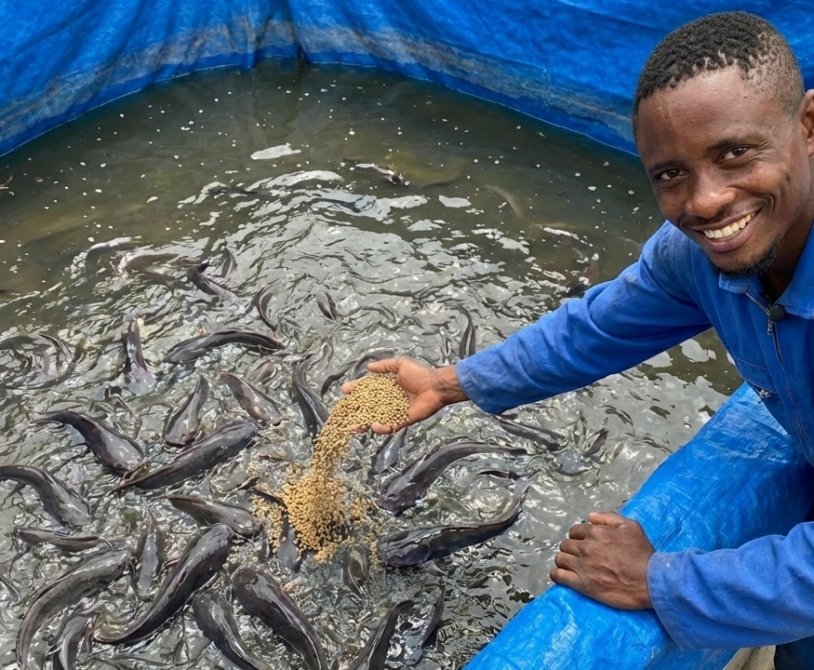

Starting a catfish agribusiness is a lucrative venture, but its success hinges on a robust financial feasibility study. Many aspiring aquaculturists fail not due to a lack of passion, but…
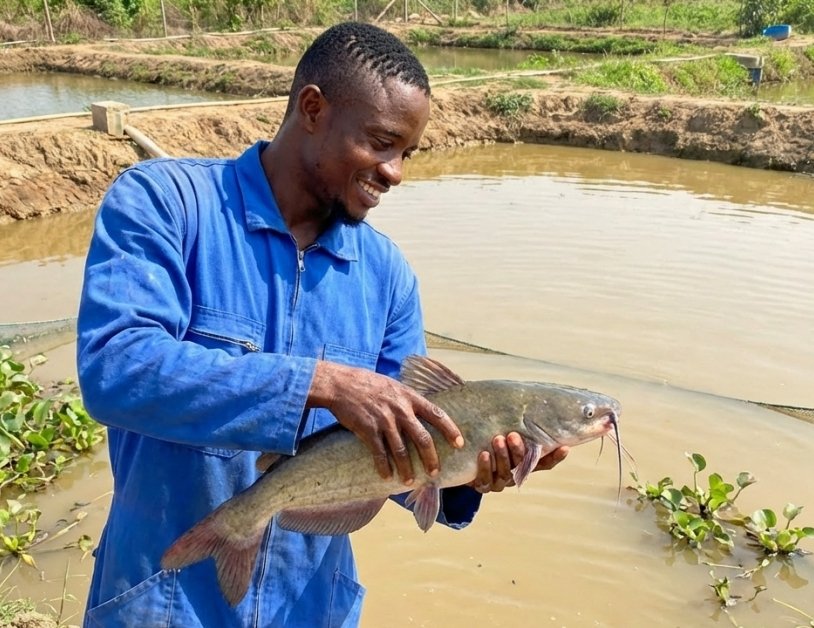

In commercial aquaculture, the cost of treating an outbreak is often ten times higher than the cost of prevention. Once a pathogen (bacteria, virus, or parasite) enters a high-density pond,…
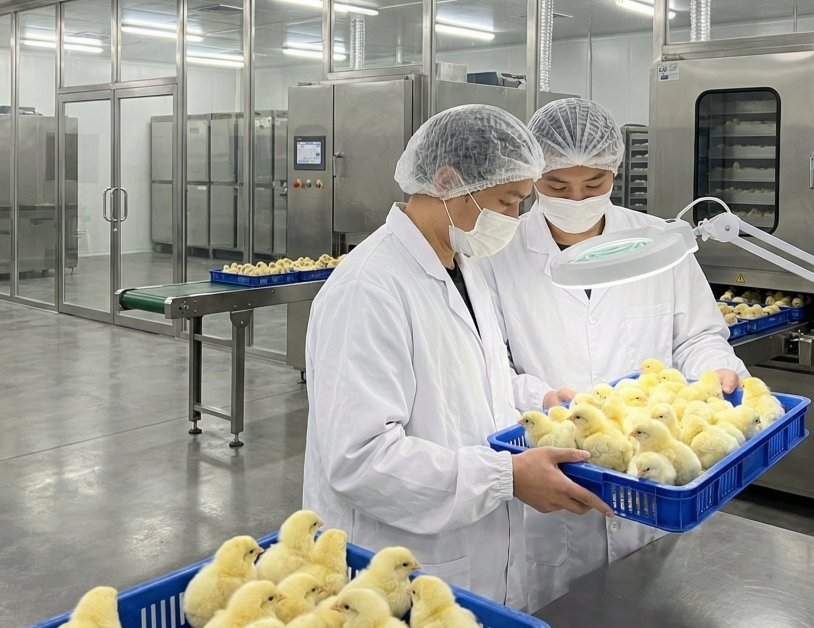

A meat chicken hatchery plays a vital role in poultry production by supplying healthy, fast-growing birds specifically bred for meat. These hatcheries are the starting point of the entire broiler…
If you’re new to poultry farming, you may be wondering what broiler chickens are and why they are so popular in meat production. Broilers are chickens specifically bred to grow…
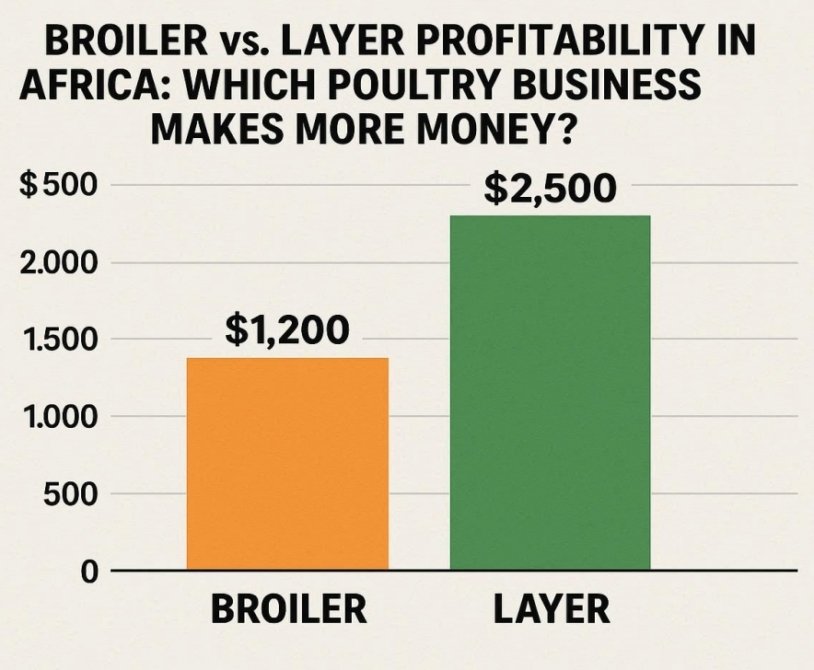
Which Poultry Business Makes More Money? Poultry farming is one of the fastest-growing agricultural businesses across Africa. With increasing demand for affordable protein, many farmers are entering the industry. However,…