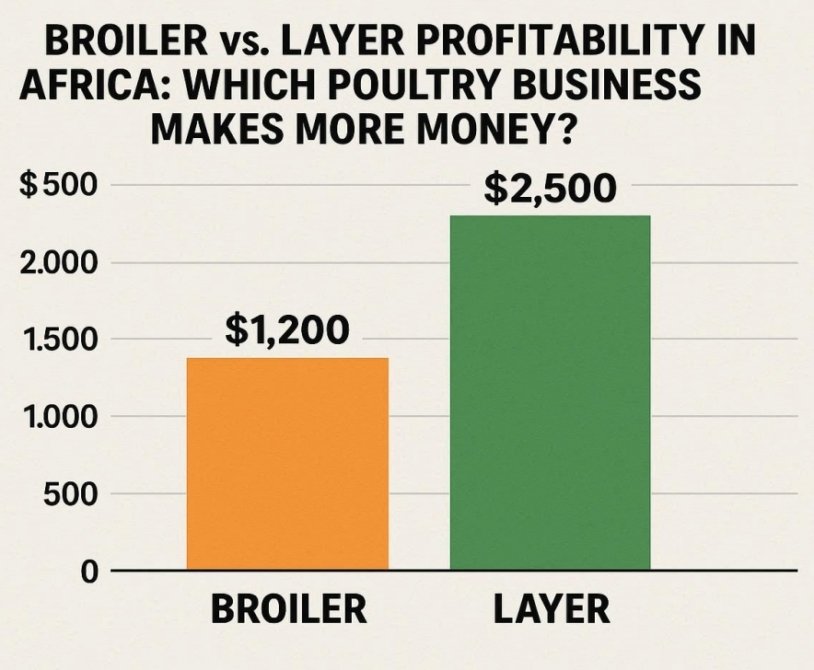
Which Poultry Business Makes More Money? Poultry farming is one of the fastest-growing agricultural businesses across Africa. With increasing demand for affordable protein, many farmers are entering the industry. However,…
Organic agricultural products right to your table!

Which Poultry Business Makes More Money? Poultry farming is one of the fastest-growing agricultural businesses across Africa. With increasing demand for affordable protein, many farmers are entering the industry. However,…

If you are planning to start a poultry farm or expand your current operation, one of the most important decisions you must make is whether to raise broilers or layers.…

Best Toppings for Egg Salad Sandwich Egg salad is a creamy mixture made from chopped boiled eggs, mayonnaise, seasoning, and optional toppings. It is commonly used as a sandwich filling,…

Banana cake is a soft, moist, and naturally sweet cake made from ripe bananas, flour, eggs, sugar, and butter. In many African homes, it is a popular snack, dessert, or…
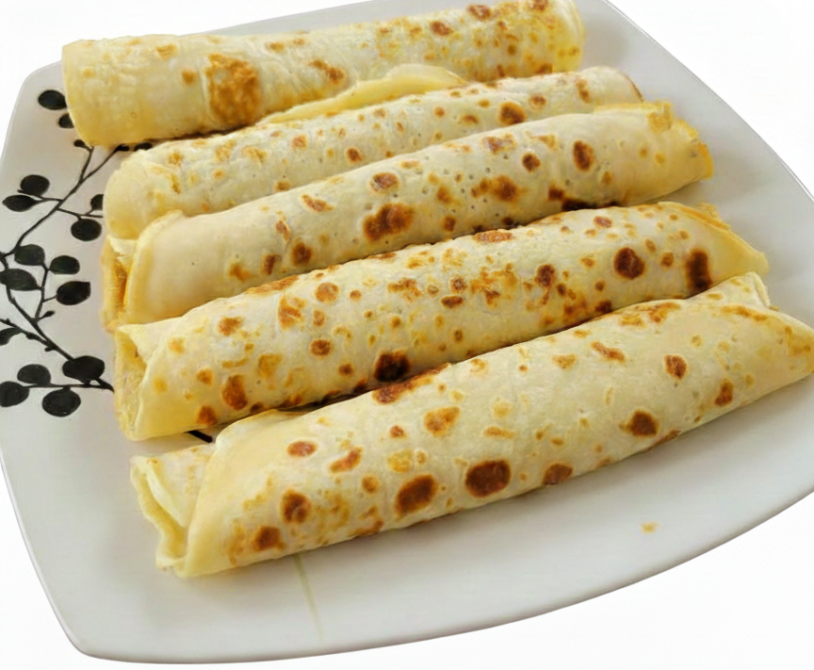

Pancakes are soft, flat cakes made from a simple batter of flour, eggs, milk, and sugar, cooked on a hot pan or griddle. They are one of the most popular…

An egg sandwich is a quick, nutritious, and easy-to-prepare meal made by combining cooked eggs with bread and simple fillings. It is popular for breakfast, lunch, and light dinners because…

How to Make Simple and Delicious Egg Fried Rice Egg fried rice is one of the easiest and most popular quick meals in the world. It is made by stir-frying…
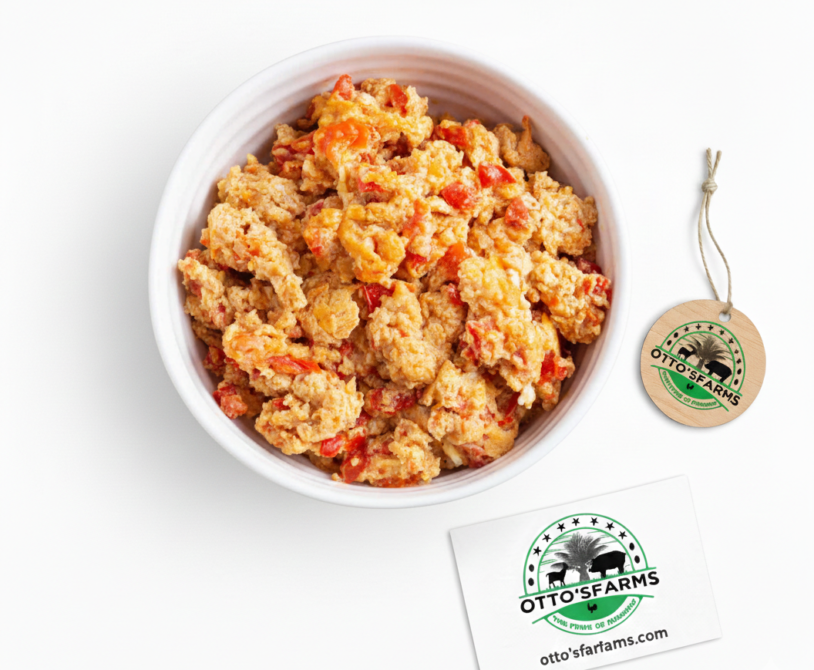

What Is Egg Sauce? Egg sauce is a popular Cameroonian dish made by cooking eggs in a rich tomato-and-onion sauce seasoned with spices. It is quick to prepare, affordable, and…

Boiled eggs are whole chicken eggs cooked in hot water until the egg white and yolk solidify. They are widely consumed worldwide because they are affordable, nutritious, easy to prepare,…
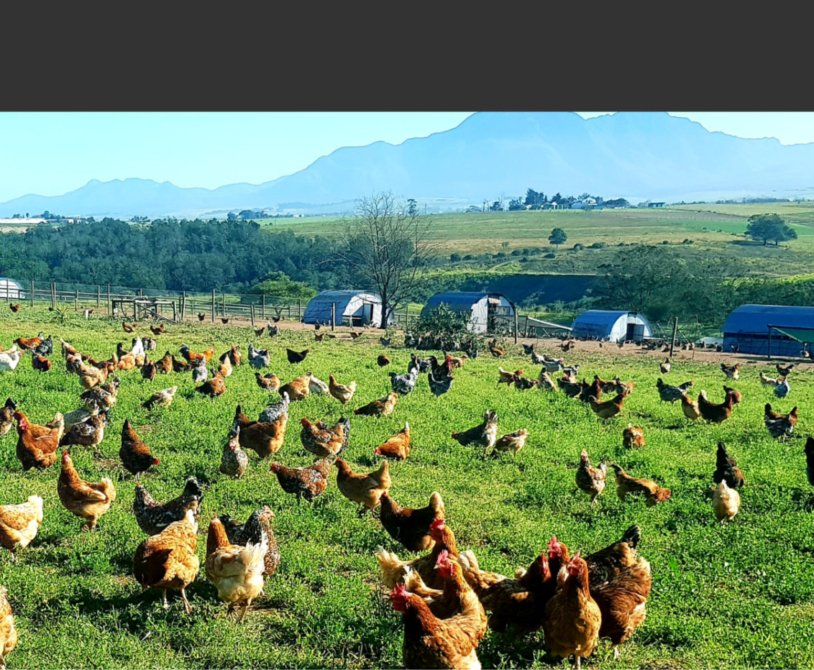

To find local poultry farms near you, you need to explore different ways to locate them. Try searching online for nearby poultry farms, asking for recommendations from friends and family,…